Astronomie stellaire
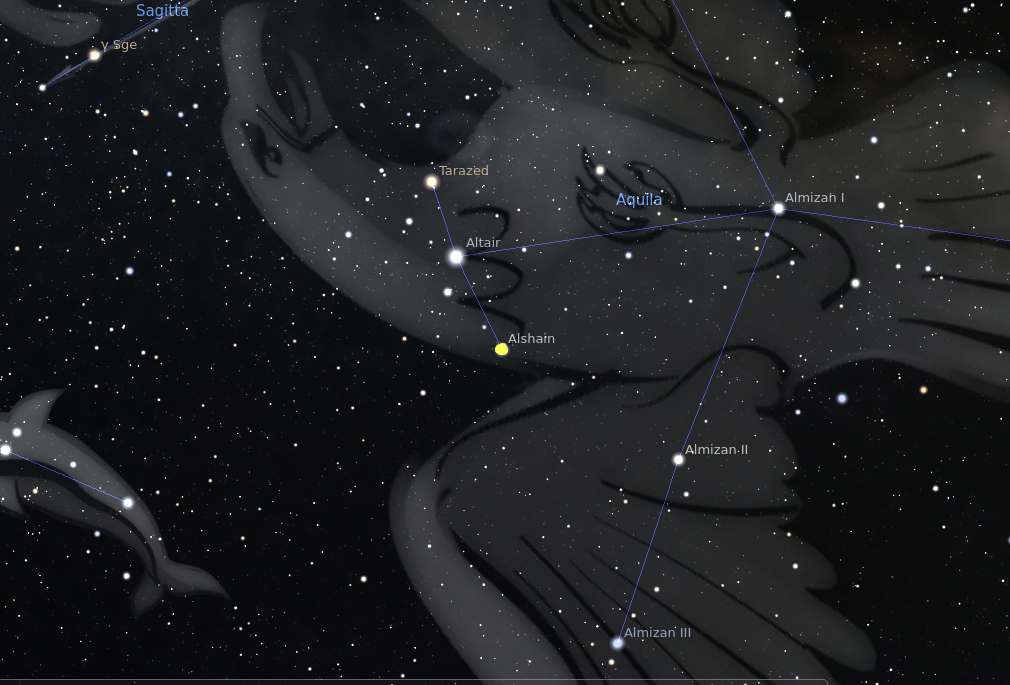
Alshain
Alshain : Un Nom Stellaire au Passé Trouble
Alshain, également connue sous le nom d'Alpha Aquilae, est une étoile de la constellation d'Aquila, l'Aigle. Bien qu'elle ne soit pas aussi largement reconnue que sa voisine plus brillante Altaïr, Alshain occupe une place unique dans l'histoire astronomique, son nom étant enveloppé de mystère et d'ambiguïté.
Un Nom aux Origines Multiples :
Le nom "Alshain" est supposé provenir de l'expression arabe "al-Shahin", signifiant "le faucon". Cela a du sens compte tenu de l'association d'Aquila avec l'oiseau de proie. Cependant, les origines exactes et l'utilisation du nom sont débattues. Certaines sources affirment qu'il s'agissait d'un nom arabe traditionnel pour l'étoile, tandis que d'autres suggèrent qu'il a été introduit par les astronomes européens à la fin de la Renaissance.
Théories Concurrente et Incertitudes :
Pour ajouter à la confusion, Alshain est parfois utilisé de manière interchangeable avec "Altaïr", ce qui conduit à un flou entre les deux noms d'étoiles. Cela complique encore le contexte historique d'Alshain, rendant difficile la détermination précise de son utilisation.
L'Astronomie Moderne et Alshain :
Malgré l'ambiguïté entourant son nom, Alshain est une étoile importante en astronomie moderne. Il s'agit d'une étoile blanche de la séquence principale, environ deux fois plus grande et massive que notre Soleil. Alshain est également une étoile variable, ce qui signifie que sa luminosité fluctue légèrement au fil du temps.
L'Avenir du Nom d'Alshain :
Bien qu'Alshain ne soit peut-être pas aussi largement utilisée que sa voisine plus brillante Altaïr, elle sert de rappel à la riche histoire et à la nature évolutive de la nomenclature céleste. Le nom de l'étoile, bien qu'un peu obscur, continue de susciter la curiosité et le débat parmi les astronomes et les amateurs d'étoiles.
En résumé : Alshain est un nom parfois appliqué à Alpha Aquilae, mais ses origines et son utilisation restent floues. Malgré l'ambiguïté, Alshain occupe une place dans l'histoire astronomique et continue de fasciner ceux qui s'intéressent aux étoiles.
Test Your Knowledge
Alshain Quiz:
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is the other name for Alshain?
a) Beta Aquilae
Answer
b) Alpha Aquilae
2. What does the Arabic phrase "al-Shahin" mean?
a) The Eagle
Answer
b) The Hawk
3. Which statement about the origins of the name "Alshain" is true?
a) It was always a traditional Arabic name for the star.
Answer
b) Its origins and usage are debated.
4. What type of star is Alshain?
a) Red Giant b) White Dwarf
Answer
c) White Main-Sequence Star
5. What makes Alshain a unique star?
a) It is the brightest star in the constellation Aquila.
Answer
b) It is a variable star.
Alshain Exercise:
Instructions: Imagine you are writing a blog post about Alshain for a website about astronomy. Write a short paragraph highlighting the fascinating aspects of this star, addressing the mystery surrounding its name and the scientific information we know about it.
Exercise Correction
Alshain, also known as Alpha Aquilae, is a star shrouded in mystery. While its name, possibly derived from the Arabic "al-Shahin" meaning "the hawk," seems fitting for its location in the constellation Aquila, the Eagle, its precise origins and usage remain unclear. This ambiguity adds to the intrigue surrounding this white main-sequence star, which is roughly twice the size and mass of our sun. Alshain is also a variable star, meaning its brightness fluctuates slightly over time. This fascinating celestial object serves as a reminder of the rich history and evolving nature of astronomical nomenclature, sparking curiosity and debate among astronomers and stargazers alike.
Books
- "Stars and Their Legends" by Ian Ridpath: This book explores the mythology and history behind various constellations and stars, including some information about Alshain and its connection to the Arabic phrase "al-Shahin".
- "Norton's Star Atlas and Reference Handbook" by Ian Ridpath and Wil Tirion: A comprehensive atlas for amateur astronomers, this book provides detailed information about constellations and stars, including Alpha Aquilae (Alshain).
- "The Cambridge Encyclopedia of Astronomy" edited by Paul Murdin: This encyclopedia offers in-depth explanations of astronomical concepts and objects, which may include information about Alshain's properties and characteristics.
Articles
- "The Names of the Stars: A Brief History" by James B. Kaler: An article exploring the history of star names, including the Arabic origins of many star names, which might shed light on Alshain's naming.
- "Alpha Aquilae (Alshain)" on the website of the International Astronomical Union (IAU): The IAU, the authority on astronomical nomenclature, may provide official information about the name Alshain and its usage.
Online Resources
- Wikipedia entry for Alpha Aquilae: This page may offer information about the star's properties and its name, though it might not delve into the historical ambiguity surrounding "Alshain".
- Stellarium software: This free planetarium software allows users to view the night sky and learn about stars and constellations. Searching for "Alpha Aquilae" in Stellarium might provide information about its name and history.
Search Tips
- Use specific search terms like "Alshain history," "Alshain etymology," or "Alshain Arabic origin" to find relevant information.
- Combine search terms with related keywords like "Alpha Aquilae," "Altair," and "constellation Aquila" to broaden your search.
- Utilize quotation marks around specific phrases like "al-Shahin" to find exact matches.
Techniques
Alshain: A Deeper Dive
Here's a breakdown of the Alshain topic into chapters, leveraging the provided text and expanding upon it with hypothetical content where necessary. Remember, much of the information about Alshain's specific properties and historical usage needs further research to verify and expand upon.
Chapter 1: Techniques for Studying Alshain
This chapter will discuss the methods used by astronomers to observe and analyze Alshain.
- Spectroscopy: Analyzing the light from Alshain to determine its composition, temperature, and radial velocity. We can discuss the techniques used, such as grating spectrometers and the interpretation of spectral lines.
- Photometry: Measuring the brightness of Alshain over time to detect variations and determine its variability characteristics. Different photometric bands (e.g., UBVRI) and techniques will be covered.
- Astrometry: Precisely measuring Alshain's position in the sky to track its proper motion and potentially detect unseen companions. The use of high-precision telescopes and interferometry will be discussed.
- Interferometry: Combining light from multiple telescopes to achieve higher angular resolution, allowing for more detailed studies of the star's surface and any surrounding environment.
Chapter 2: Models of Alshain
This chapter delves into theoretical models used to understand Alshain's properties and evolution.
- Stellar Evolution Models: Using theoretical models to predict Alshain's age, mass, and future evolution based on its current characteristics (luminosity, temperature, etc.). The limitations and uncertainties of these models will be discussed.
- Atmospheric Models: Constructing models of Alshain's atmosphere to explain its observed spectral features and variability. This would include considerations of temperature gradients, chemical abundances, and convection.
- Hydrodynamic Models: Simulating the physical processes occurring within Alshain, such as convection, rotation, and magnetic activity, to understand its variability and overall behavior.
Chapter 3: Software Used in Alshain Research
This chapter explores the computational tools used to analyze Alshain data.
- Data Reduction Software: Packages like IRAF (Image Reduction and Analysis Facility) or specialized software for telescope control and data acquisition would be discussed.
- Spectral Analysis Software: Programs used to analyze spectroscopic data, such as fitting spectral lines and determining chemical abundances.
- Modeling Software: Software packages for stellar evolution, atmospheric, and hydrodynamic modeling. Examples might include MESA (Modules for Experiments in Stellar Astrophysics) or other specialized codes.
- Statistical Software: Software for data analysis and statistical modeling, such as R or Python with relevant packages.
Chapter 4: Best Practices in Alshain Research
This chapter outlines the best practices for conducting research on Alshain.
- Calibration and Error Analysis: Emphasizing the importance of proper calibration procedures and rigorous error analysis in all measurements and models.
- Data Validation and Quality Control: Methods for ensuring data quality and identifying and correcting potential systematic errors.
- Peer Review and Collaboration: The crucial role of peer review and collaborative research in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of results.
- Data Archiving and Sharing: Best practices for archiving and sharing research data to facilitate reproducibility and future research.
Chapter 5: Case Studies of Alshain Research
This chapter presents examples of past and ongoing research on Alshain (assuming such research exists and can be sourced. This section will be largely hypothetical as detailed research on Alshain specifically is not readily available). Examples might include:
- Case Study 1: A hypothetical study on Alshain's variability using long-term photometric data. The methods, results, and conclusions would be discussed.
- Case Study 2: A hypothetical spectroscopic study to determine the chemical composition of Alshain's atmosphere and compare it to other similar stars.
- Case Study 3: A hypothetical study investigating the potential for planets orbiting Alshain using radial velocity measurements.
This framework provides a structured approach to exploring Alshain, even with the limited readily available information. Remember to replace hypothetical content with actual research findings once they are obtained.
Comments